What is the Xen Project?
Xen Project creates a software system, that allows the execution of multiple virtual guest environments simultaneously on a single physical machine. It is valuable when you want to create a complex security software system consisting of several operating systems. Unprivileged domains (domUs), such as virtual operating systems have no direct access to the hardware.
Between software and hardware is a hypervisor. It allocates resources for new domains (the virtual operating systems) and schedules the existing ones. To learn more about hypervisor see the official documentation.
What is Domain0?
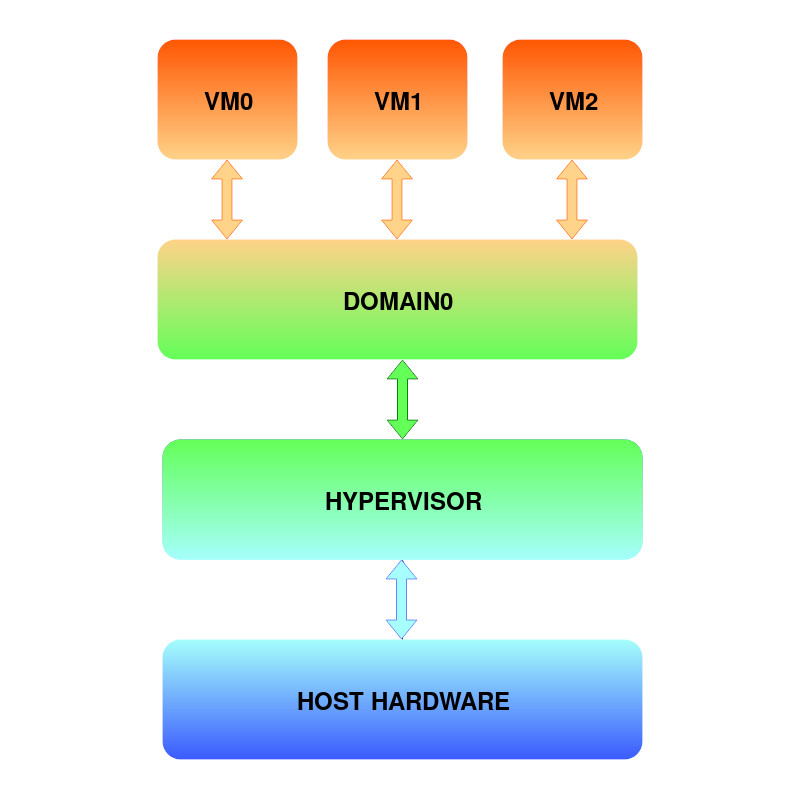
As shown in the figure, domain0 (dom0) is the privileged domain, which manages unprivileged domUs. Dom0 is started by the hypervisor at the boot and ensures its usability. Therefore the dom0 has direct access to the hardware. The Domain0 provides hardware connections to domUs. Depending on the guest type, dom0 allows hardware virtualized guests (HVM) to use emulated hardware. In the case of paravirtualized domains (PV), the dom0 connects the domUs with the hardware via backend and the drivers. Here is more information about Virtualization Spectrum
How to build Dom0 on the PC Engines apu2?
We will use the meta-pcengines repository. to build the special domain for the PC Engines apu2 board. The repository contains the yocto layer, that allows you to create a minimal image of the dom0. The meta-pcengines uses a kas tool to build the dom0 image. Installation, configuration, and some more information about this tool you can find in the previous blog.
Once you have installed the kas, clone the meta-pcengines repository. To reproduce my results, check if the source commit matches shown above. The source consists of configuration files, a kas configuration file, and recipe files. The layer configuration specifies settings for the platform and distro It points out where the recipes are placed. The kas configuration file is used by the kas tool to clone and checkout Yocto layers. It also allows kas to create default BitBake variables such as MACHINE, DISTRO, etc.
Now it is time to create the build. Move to the meta-pcengines parent directory and enter the command:
|
|
The dom0 image build process can take several hours, so you can take a coffee break. Once the build is finished, you will see a similar output:
|
|
At this point, create a bootable USB drive. Change the directory to
<build-dir>/build/tmp/deploy/images/pcengines-apu2 and replace sdx in below
command with the device node of your USB flash drive.
|
|
Once you have created the bootable drive, try to boot your platform. The following video shows the correct bootlog:
Guest VM configuration
Once you have booted the dom0 on your apu2 platform, it is time to launch a VM guest. At first write the config file, where you will set up the guest domain options. Here is an example:
|
|
You have to set the name of your new guest domain. In the disk variable,
point the path of the image guest image. A detailed description of each variable
is given on the
xenbits website.
Create the VM guest with the command:
|
|
The following output shows the boot process of the domU:
Conclusions
The main goal of the meta-pcengines is to enable Yocto builds for pcengines (apu2) boards. It provides a good base for various use cases such as Xen. In future blogs, we will show more application examples. So if you are interested, sign up for our newsletter:
