Requests library is one of the most popular libraries implemented for Robot Framework. It is very important for testing distributed applications, so this is the first library I got to know in the Robot Framework.
To test Request library we can install Pi-GPIO-Server on Raspberry Pi. The
server is able to control the state of input and output of GPIOs using REST API.
The project is available on the link: Project weekend - GPIO Server
In the REST API we used following methods:
- Delete
- Get
- Options
- Post
- Put
- Patch
To control GPIOs on the RPI we need only Get and Patch methods, other
methods are used in the same way - Options is used for exceptions.
I assume you have already installed Robot Framework. If the response is “NO”, I
would encourage you to read the Installation paragraph It is official
documentation for Robot Framework. Next, we can install requests libraries.
Collections library is a standard built-in library. Use below commands to
install libs.
|
|
RASPBIAN STRETCH WITH DESKTOP from download link. It is a very good
solution because we can control also GPIOs using buttons.

I hope that instruction of installation process is sufficient, so I will not duplicate the description. Take a few minutes to prepare the pin configuration and restart gpio server:
|
|
For running server go to Pi-GPIO-Server and type:
|
|
Now, we can start writing code for GPIO control using REST API and Robot Framework.
|
|
Run RPi and check for its IP address. We will use IP for connection with API
server. My RPI has IP: 192.168.0.46. The documentation says that server runs on
5000 port. So we can prepare URL variable. On Variables section type:
|
|
Let’s run the first test
Get signals. Firstly we should create a session for request control in Robot
Framework. To create the session we use the keyword Create session with
parameters alias, URL and optional verify. How to create session
|
|
We will use alias for all keywords which work on URL. All sessions should be
closed using the keyword Delete All Sessions. Next, we need a header, which
should be sent with the request. One of the methods for creating header looks
like:
|
|
A good trick is assigning headers to the variable. To check the value of GPIO, special GET method is prepared. Documentation tells:
|
|
Let’s implement it in another way:
|
|
As I said, alias is very important because it defines on which session we send
requests. For observing results Robot Framework has special keyword. Its name is
Log.
Whole test look like this:
|
|
To get all signals you can only type hyperlink without the pin number. Example:
|
|
That was the easier part of our script.
To set a high or low state for GPIOs you should use patch method. The first
step is creating a dictionary with value to send. It is not difficult:
|
|
Patch request requires message data to send.
|
|
We can use the same test to set the high state on GPIO. As an indicator, I used LED diodes and resistors in series connection.
The full version of my code:
|
|
This code is not in perfect form, but it’s not the subject of this article. So polishing is left to the reader. RF generates very readable reports after all tests are done.
Reports look like this:
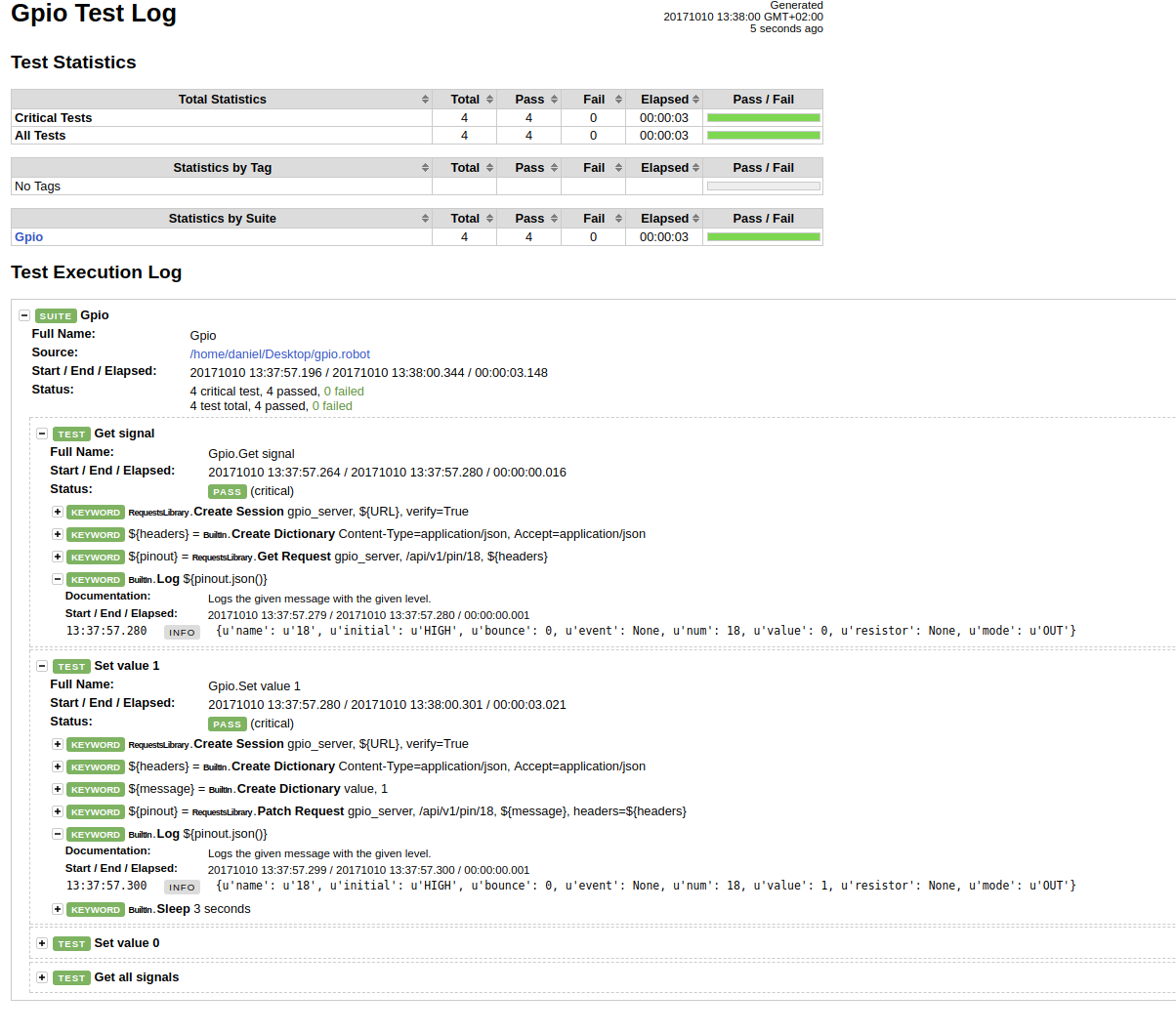
You can see that Robot Framework is very easy to use environment for testing
REST API. All methods (e.g. POST and Patch) are the same in use. If you need
help with implementing tests you can ask me or chat with users on Slack
-requests channel on the robot-framework group. I help new users, whenever I
can, and also sometimes I’m the one looking for help.
